Car Seat Safety by Dr. Amit Jain, Pediatrician
We here at NOAH care about your child’s health and safety not only at the clinic, but at home and on the go too. One very important part of this is Car Seat Safety. We would like to remind you about the importance of Car Seats, and how to keep your child safe when on the go.
Especially for a new parent, the variety of car seats available today can be overwhelming! And it makes it more difficult to make sure your child is buckled in appropriately. We would like to help alleviate some of the confusion! Thinking about a car seat starts before your child is born. Most hospitals require an appropriate car seat for you to take your baby home and do car seat checks when your new baby is first allowed to go home from the hospital.
Unintentional injuries (including car accidents) are the leading cause of death in children and teens. Courtesy of the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), we know that on average, 3 children were killed every day in traffic accidents. Of those, more than a third of the children were unrestrained. More than half of injuries and deaths were cases in which car seats and seatbelts were incorrectly used.
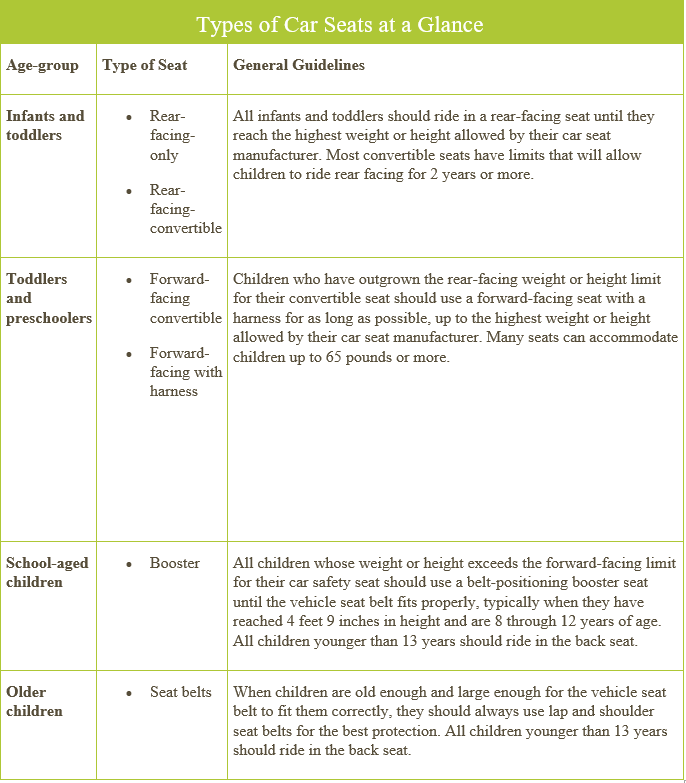
There are various types of car seats to consider based upon your child’s age, weight, and height including rear-facing, convertible (rear-facing that can become forward-facing), forward-facing, and booster seats (with or without back support). Below is a chart explaining the various car seats, separated by age group. To securely install these various car seats, you can either use the available seatbelts or the LATCH system. Nearly all vehicles and car seats built after September 1, 2002 include this LATCH system (Lower Anchors and Tethers for Children) which consists of a lower anchor where the seat cushions meet, and a tether which can be located on the panel behind the seat, on the back of the seat, the ceiling, or the floor.
Some important points when using these systems:
- Most rear-facing car seats do not use the tether for installation, just the lower anchor and/or seatbelt.
- You should not use both the lower anchor and seat belt together unless specifically instructed in the car seat installation instructions. However, the tether can and oftentimes will be used along with the seatbelt to securely install the seat.
- To get a tight fit using the seatbelt, the seatbelt should lock. For most modern cars, the seatbelt can be locked by pulling it out all the way, and then letting it retract as it clicks.
- When possible, the middle back seat is the safest. However, the middle seat often doesn’t have a LATCH system, or is too small, or uneven to safely support a child. It is most important that wherever the child may be seated, that the seat is securely and tightly installed in the vehicle.
- Infants and children should wear thinner clothes when buckled into car seats as bulky clothing such as jackets can leave the straps too loose, increasing the risk for injury.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all infants be placed in rear-facing car seats starting from their first ride home from the hospital.
- All infants and toddlers should ride rear-facing as long as possible (even if their legs are bent), until the highest weight or height allowed by their car seat.
- When children outgrow their rear-facing only car seat, a convertible car seat installed rear-facing should be used.
- A forward-facing car seat should be used only once a child has reached the weight or height limit for their convertible rear-facing car seat. Similarly, a forward-facing car seat should be used until the weight or height limit for that specific car seat has been reached (this is usually listed on the label of the car seat).
- A belt-positioning booster seat is the next step and should be used until a child’s seatbelt fits properly across their shoulder (without riding up to their neck), which is typically at a height of 4 feet, 9 inches or taller, and 8-12 years of age.
- The safest place for all children younger than 13 years old is the backseat.
- Do
NOT use the car seat after it has been in a moderate to severe crash, such as
if any of the following are true (according to the NHTSA):
- The vehicle could NOT be driven away from the crash
- The vehicle door closest to the car seat was damaged
- Anyone in the vehicle was injured
- The airbags went off
- There is any significant damage to the car
And remember, always be a good role model by buckling your own seatbelt every time you’re in the vehicle! Set a reminder whenever you buckle your child’s car seat to help you remember never to leave your child in or around your car when you leave.
If you need help installing your child’s car seat, or just want to make sure it is secure, below are some great options for you to reach out to:
- Your local fire department
- Parent partners plus
- Phoenix Children’s Hospital car seat safety program
For more information, please visit:
- The American Academy of Pediatrics Healthychildren.org and https://www.healthychildren.org/English/safety-prevention/on-the-go/Pages/Car-Safety-Seats-Information-for-Families.aspx
- The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration website (https://www.nhtsa.gov/equipment/car-seats-and-booster-seats)